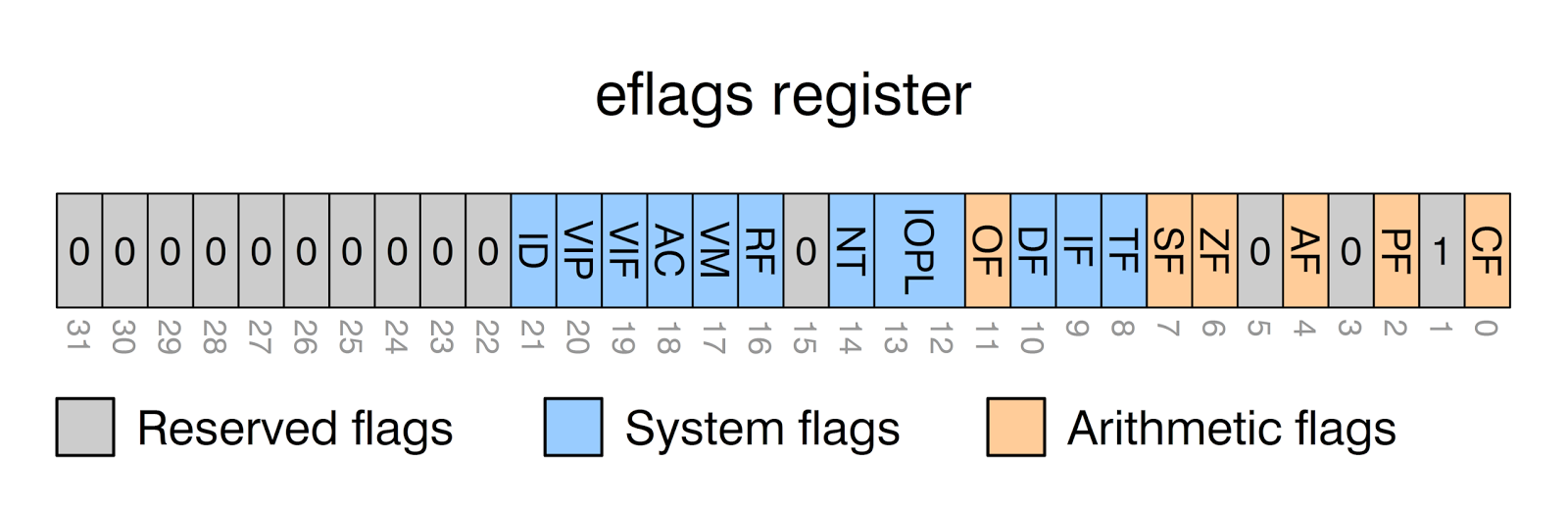
Flags¶
Flags are used to signify the result of the previously executed operation or comparison. For example, if two numbers are compared to each other the flags will reflect the results such as them being even.
Flags are contained in a register called EFLAGS (x86) or RFLAGS (x64). There is a FLAGS register that is 16 bit.
These flags are bits in a special register known as the flags register or EFLAGS register.
| Flag | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
CF |
Carry Flag | Set if the last unsigned arithmetic operation carried (addition) or borrowed (subtraction) a bit beyond the register. It's also set when an operation would be negative if it wasn't for the operation being unsigned. |
OF |
Overflow Flag | Set if a signed arithmetic operation is too big for the register to contain. |
SF |
Sign Flag | Set if the result of an operation is negative. |
ZF |
Zero Flag | Set if the result of an operation is zero. |
AC |
Adjust or Auxiliary Carry | Same as the carry flag but for Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) operations. |
PF |
Parity Flag | Set to 1 if the number of bits set in the last 8 bits is even. (10110100, PF=1; 10110101, PF=0) |
TF |
Trap Flag | Allows for single-stepping of programs. |
DF |
Direction Flag | |
IF |
Interrupt enable |