Basics¶
Entry point¶
C#'s Entry point, like other languages is the Main function. It's the function that gets ran first whenever we start the program. For now there's no need to worry about static, void or string[], it's unimportant.
Take a look at the picture below, this is what a typical C# program looks like at first:
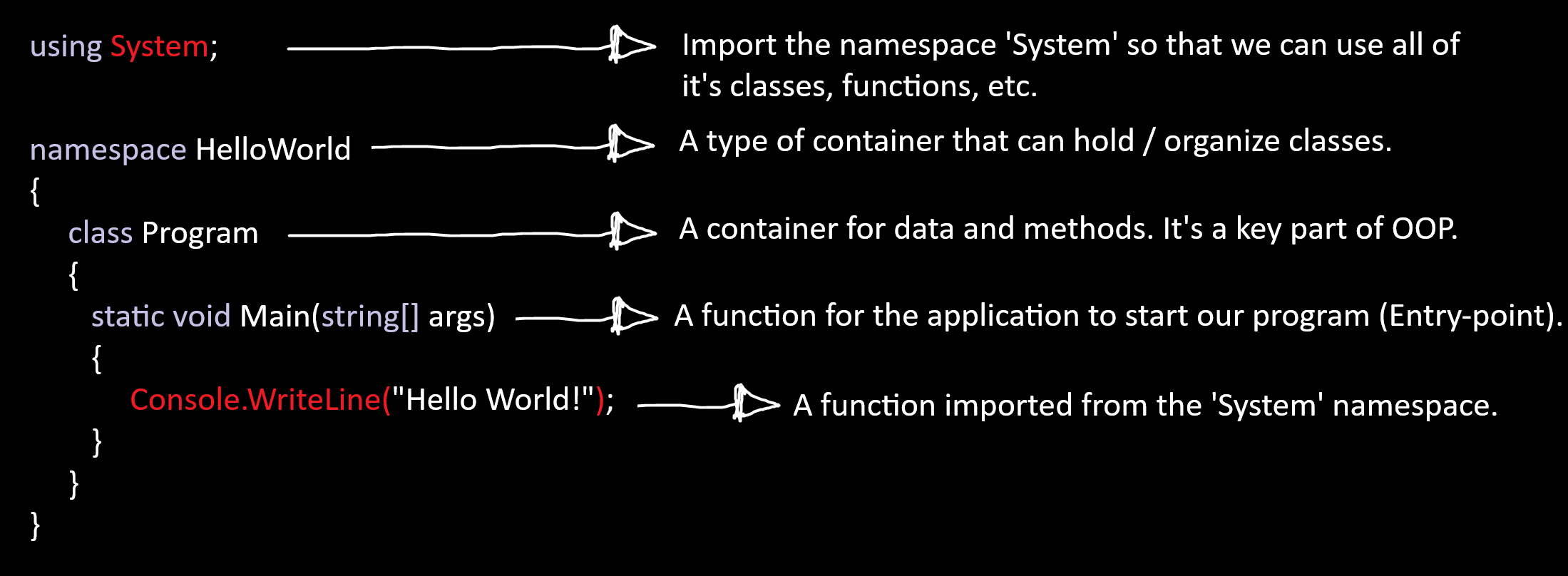
Data types¶
Variables are a container for us to store a value that belongs to a data type. There's two different types of value types: value and reference.
If you want to know more:
- Value types store the actual value directly.
- Reference types store a reference (memory address) that points to the value.
We can use built-in types that are defined by the language or build these data types ourselves. Sone of these types like the user-defined reference types will seem complicated at first, know that they're unimportant for now.
Value types¶
Predefined:
| Real-word type | According C# keyword | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Whole numbers | int |
-5 or 5 |
| Floating point numbers | float or double |
-5.5 or 5.5 |
| Letters | char |
'A' or 'z' |
| Validity | bool |
true or false |
User-Defined:
| Real-word type | According C# keyword | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A lightweight type for grouping others. | struct |
struct Point { public int X, Y; } |
| A set of names constant values. | enum |
enum Days { Monday, Tuesday } |
Reference types¶
Predefined:
| Real-word type | According C# keyword | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sentences (collection of letters) | string |
"Hello World!" |
| A 'thing', any thing. | object |
"Hello World!" or 5.5 |
User-Defined:
| Real-word type | According C# keyword | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A constructed object that can do things. | class |
class Dog{} |
| A contract / rules for objects on how to behave. | interface |
interface Dog{} |
| A reference to a function. | delegate |
public delegate int PerformCalculation(int x, int y); |
Variables¶
Wokring with variables throughout our program we will often change their values. However, we also somewhat keep track of their state.
A variable can be declared without a initial value:
int a;
Note that some types will get defaulted to a initial value like 0.
A variable can be assigned a value:
a = 5;
A variable can be initialized (declared with a value):
int a = 5;
Operators¶
We can perform some calculations or variables or literal values using operators.
There's a bunch of types of operators. Usually when thinking of operators we think of Arithmetic operators like plus.
For example: int a = 5 + 5; or int b = a + 5; or int c = a + b;
Arithmetic¶
| Name | Operator |
|---|---|
| Addition | + |
| Subtraction | - |
| Multiplication | * |
| Division | / |
| Modulus | % |
| Increment | ++ |
| Decrement | -- |
Assignment¶
| Name | Operator |
|---|---|
| Assignment | = |
| Addition assignment | += |
| Subtraction assignment | -= |
| Multiplication assignment | *= |
| Division assignment | /= |
| Modulus assignment | %= |
Comparison¶
| Name | Operator |
|---|---|
| Equal to | == |
| Not equal to | != |
| Greater than | > |
| Less than | < |
| Greater than or equal to | >= |
| Less than or equal to | <= |
Logical¶
| Name | Operator |
|---|---|
| Logical AND | && |
| Logical OR | \|\| |
| Logical NOT | ! |